Purpose and objective of separate collection of packaging waste
At Interzero, we promote the proper separation of packaging waste at source, i.e. at the waste generators – distributors and end-users.
According to the Waste Regulation, the types of packaging waste are classified into the following groups: 15 01 01 – paper and cardboard packaging, 15 01 02 – plastic packaging, 15 01 03 – wooden packaging, 15 01 04 – metal packaging, 15 01 07 – glass packaging, 15 01 10* – packaging containing residues of or contaminated with hazardous substances, 15 01 11 including empty pressure containers.
The aim of the separate collection system is to ensure that packaging waste does not end up in mixed waste, but is diverted for recovery. Packaging fractions collected separately can be used to produce useful secondary raw materials. All stakeholders need to be aware of the importance of following the environmental targets set out in the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation, i.e.:
1. recovery of packaging waste, including energy recovery, must be ensured for at least 60 % of the total weight of packaging waste;
2. between at least 55% and no more than 80% of the total weight of packaging waste must be recycled;
3. for each type of packaging material contained in the total weight of packaging waste, at least the following recycling rates must be ensured: a) 60 per cent of the weight for glass, b) 60 % of the weight of paper and paperboard, c) 50 per cent by weight for metals, (d) 22,5 % by weight for plastics, taking into account only material that is recycled back into plastics, e) 15 per cent by weight for wood.
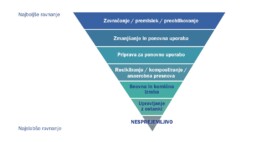
And we achieve our goals through continuous awareness-raising. We carry out separate packaging waste collection inspections at companies, advising on the correct separation of packaging fractions so that the most uniform and clean materials are recovered in subsequent recycling processes. As an individual, you can play an active role in reducing the burden on the environment, including by knowing the general waste hierarchy. In addition to proper segregation, preventing packaging waste is an important link to achieving the targets. When shopping, pay attention to the packaging of the product, buy thoughtfully and buy things you need, and only throw away items that cannot be repaired, reused or donated.
Purpose and objectives of separate collection of waste EE equipment
At Interzero, we promote the proper separation of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) at source, i.e. from waste generators – distributors and end users.
Electrical and electronic equipment is divided into six classes:
- Heat exchange equipment
- Displays, monitors and display equipment with a surface area greater than 100 cm2
- Lightbulbs
- Large equipment (any external dimension greater than 50 cm)
- Small equipment (no external dimension larger than 50 cm)
- Small IT and telecommunications equipment (no external dimension larger than 50 cm)
It is collected separately in five collection and processing groups:
- Waste large household appliances (any external dimension greater than 50 cm); washing machine, dishwasher, tumble dryer, electric cookers, drinks dispensers, cash dispensers, lawnmowers, etc.
- Waste cooling and freezing appliances; fridge, freezer, air conditioner, etc.
- Waste TV sets, monitors and picture tubes; TV sets, laptop screens, LCD screens, etc.
- Waste small electrical and electronic equipment (no external dimension larger than 50 cm); vacuum cleaner, hairdryer, el. toothbrushes, toys containing batteries, irons, coffee machines, toasters, kettles, alarm clocks, wristwatches, scales, drills, saws, sewing machines, video games, telephones, video cameras, radios, hand-held games consoles, electric trains and cars, medical devices, etc.
- Waste lamps; fluorescent rod lamps, compact fluorescent lamps, high intensity discharge lamps, low pressure sodium vapour lamps, led lamps, etc.
The aim of the separate collection system is to ensure that WEEE does not end up in mixed waste but is diverted for recovery. Properly separated WEEE can be used to produce useful secondary raw materials.
- WEEE collection must collect a minimum amount of WEEE per calendar year of:
from 2021, at least 65% of the average weight of EEE placed on the market in the RS annually in the preceding three years, or 85% of the average weight of WEEE generated annually in the RS.
- From 1 January 2018, the treatment of separately collected WEEE must ensure that the amount and method of recovery are such that:
- recover 85 % and prepare for re-use and recycle 80 % of WEEE classified as Class 1 or 4
- recover 80% and prepare for re-use and recycle 70% of WEEE classified as Class 2
- recover 75 % and prepare for re-use and recycle 55 % of WEEE classified as Class 5 or 6
- recycles 80% of WEEE classified as Class 3
We work to achieve proper WEEE management through continuous awareness-raising.
We carry out separate WEEE collection inspections at companies and advise on proper separation.
As an individual, you can play an active role in reducing the burden on the environment, including by knowing the general waste hierarchy. In addition to proper separation, preventing the generation of WEEE is an important link to achieving the targets. When shopping, pay attention to the lifetime of electrical equipment, buy wisely and buy things you need, and only throw away products that cannot be repaired, reused or donated.
Purpose and objectives of separate collection of waste batteries
At Interzero, we promote the proper separation of waste batteries at source, i.e. from waste generators – distributors and end users.
According to the Regulation on the management of batteries and accumulators and waste batteries and accumulators, batteries are classified into 3 main groups:
- Waste portable batteries and accumulators
- Waste industrial batteries
- Waste car batteries
The aim of the separate collection system is to ensure that waste batteries do not end up in mixed waste but are diverted for recovery. Properly separated batteries can be used to produce useful secondary raw materials.
All stakeholders need to be aware that it is important to pursue environmental targets, i.e. a collection rate for portable batteries of no less than:
- 45% by 26. September 2016
Purpose and objectives of separate collection of waste funeral candles
At Interzero, we promote the proper separation of waste grave candles at source, i.e. at the waste generators – the end users.
The aim of the separate collection system is to ensure that grave candles do not end up in mixed municipal waste but is diverted for recovery. From properly separated collected waste candles, useful secondary raw materials can be recovered.
All stakeholders need to be aware of the importance of achieving the following environmental objectives, which are laid down in the Waste Grave Candles Regulation:
- recovery of waste grave candles, including energy recovery, for at least 80 % of the total weight of waste funeral candles collected;
- recycling of at least 55 % of the total weight of waste candles collected, with recycling rates of:
- 50% by weight for metals,
- 22.5% by weight for plastics, taking into account only material that is recycled back into plastic;
- from 1 January 2026 recycling of at least 65% of the total weight of waste candles collected on 1 January 2026, with recycling rates of:
- 70% by weight for metals,
- 50% by weight for plastics, taking into account only material that is recycled back into plastic;
- from 1 January 2031 recycling of at least 70 % of the total weight of waste candles collected by 2031, with recycling rates of:
- 80% by weight for metals,
- 55% by weight for plastics, taking into account only material that is recycled back into plastic.
Individuals can play an active role in reducing the environmental impact of litter by consistently separating and, above all, thoughtfully lighting candles in cemeteries.
